|
 |
 |
|
|
HEALTHFUL
SMILE
|
|
|
Author :
Dr. Isabel C. Camões
Surgeon – Dentist
CRO 11.540
General Garzon Street, 22 – 501 –
Jardim Botânico 22.470-010 –
Rio de Janeiro – RJ
Phones/Fax : (21) 2274-5228/3205-7542 E-mail
:icamoes@netbotanic.com.br |
|
A
HANDY FOR A HEALTHFUL SMILE |
|
 |
DEAR
PATIENT,
This
guide was developed to assist it in
the care with its buccal health! Here
you he will find important information
for the prevention of the carieses
and the illnesses of the gengiva.
We
remember that the prevention is so
important how much the treatment,
therefore is what it prevents that
the problems occur.
Therefore,
always that it will be with some doubt,
it counts on us to clarify it. We
want to see its pretty and always
healthful smile! |
|
|
 |
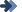
CAVIT
The cavity is one of the more frequent
dental illnesses. Generally , it elapses
of an inadequate diet, deficient buccal
hygiene and the consequent accumulation
of bacterial plate.
To prevent the cavities , it is enough
to reduce the frequency of ingestion
of sugars and to acquire the habit
to make a correct hygienic cleaning
after all the meals.
|
|
|
 |
BACTERIAL
PLATE and the illnesses of the gum
The bacterial plate is nothing more
than an accumulation of alive bacteria
and food residues that are deposited
on teeth. It is the main factor that
causes the illnesses most common of
the buccal socket (gengivitis and
periodontitis).
When there is not a good brushing,
, the bacterial plate accumulates
itself and it can infiltrate between
teeth and the gum, causing bleeding,
redness and swell, that are the main
symptoms of the gengivitis.
This infiltration can be drawn out
still more and if harden, forming
the tartar.
Together with the bacterial plate,
the tartar can aggravate the gengivitis
, dislocating the tooth of the gum,
thus compromising the osseous structure
(periodontitis symptoms), that can
to cause the fall of the tooth.
|
|
|
 |
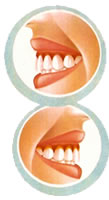
USE
A BRUSHING TECHNIQUE ADUSTED
Locate the brush in an angle of 45º
on the outside surface of all the
inside teeth, at the line of the gum
and make movements from the gum to
the direction of the tooth.
|
| In
the inside surface of teeth in front
of the mouth, also use the brush in
vertical line with movements from the
gum to the direction of the tooth. |
| In
the surface of chew of teeth, use the
brush in the horizontal line with movements
of seasaw. |
Divide
equally the time of brushing between
teeth: brush during 10 seconds each
group of 2 teeth.
Finally, brush the above part of the
tongue. |
|
|
 |
THE
IMPORTANCE OF WIRE OR DENTAL RIBBON
The brushing is not sufficient to
leave teeth free of the bacterial
actions. The use of dental wire is
basic for the removal of the bacterial
plate and food residues that are between
teeth, places where the brush does
not reach.
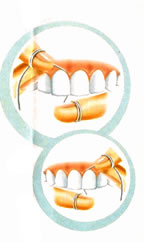
To use the
dental wire adequately, cut a piece
of approximately 45 cm and hold it
with the index-finger and thumb. Bend
the wire in the lateral of the tooth
and put it up into motion up and down,
sliding carefully on the line of the
gum. Clean the tooth of the left and
of the right of each space.
IMPORTANCE OF FLUORINE
The dayly fluorine use is very important
in the combat to the carieses. The
fluorine leaves stronger the surface
of the tooth (enamel),creating a protective
barrier. It protects teeth of the
acid attacks of the bacterial plate,
that can provoke dental illnesses,
as the caries and the gengivitis.
There are various
types of fluorine and we will study
the most adequate for your case. |
|
|
Best
Regards,
Dr. Isabel C. Camões
|
ACTION OF FLUORINE
IN THE MOUTH |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
before the buccal acid attack
|
broken by the buccal acid
|
remineralized or reconstructed
by fluorine and minerals of the saliva |
|
| *
The enamel of teeth is solid and consists
of the junction of some mineral filaments.
* When the individual eats, the bacteria
gifts in the mouth forms acid that penetrate
in the interior part of the enamel, corroding
it. It is the demineralization process.
* The demineralization can form a weak point
which degenerates in caries, if it will
not be treated.
* The fluorine speeds up the remineralization
process, softerning the enamel in addition
and preventing the formation of the caries.
See :
http://fiodental.7p.com/html/c_rie_fl_or.htm |
|
SMALL
HISTORY OF FLUORINE |
|
| The old miners had observed this mineral with very beautiful and varied colors, later named Fluorite.
The Fluorite is one of the rare minerals that are found in natural state in samples with relatively perfect crystallization and with extraordinary diversity of coloration . The cut of crystals is perfect.
The Fluorite is found in massive and granulated aggregates.
The same crystal or the same added can present diverse colors.
Fisical State : The Fluorine
is a gas.
Primary source
: The Fluorine ,also called Fluor
, has its principal source in the mineral
Fluorite .
The name
Fluorine : This denomitation is
derived from Fluorite word, that is the
denomination of its primary source .
The name
Fluor : This denomination comes
from the Latin Fluere that means to drain,
and it has origin in the liquid state of
the calcium fluorid, one of its composites,
used as solvent.
|
|
Some examples of Fluorite :
|
 |
 |
|
Blue
Fluorite with calcite crystal
budding in the center
Source : http://emineralshow.com/images/fluorite_hardin66b
|
Green Fluorite transparent
and semitransparent
Source
: www.mineralminers.com
|
|
 |
 |
|
Orange Fluorite and quartz
with crystal budding in
return
Sourse: http://glimmerdream.com/closeup/other/1/fluor
|
Fluorite
and lead-glance with ironstone
all involved with budding
crystal
Source: http://weardalerocks.com
|
|
|
|
Dental
use : The fluorine or fluor is
used as element of protection against carieses
in dental creams in the form of sodium fluoride
(NaF) or tin fluoride (SnF2 ) , and in applications
in doctor’s office or dentist specialist.
The process
: It is basically the process used for Moisson
- by electrolysis of the acid hydrofluoric
(HF) with hydrofluoric of potassium (KF2)
.
Author of
the discovery : The element fluorine
was isolated in 1866 for Henri Moisson,
French chemistry, after 74 years of attempts
of other researchers. For this discovery
he received the Nobel Prize of Chemistry
from 1906.
Composed
of Fluorite : Under the Chemistry
view, fluorite is fluorid calcium and its
crystals, completely cubical, transparent
or translucent and under certain conditions
it shows fluorescence.
Popularity
: After the Quartz, the Fluorite is the
most popular mineral in the world. The most
popular fluorite is the purple , that competes
with beautiful reds of the Amethyst. Other
colors : blue, green, yellow, colorless,
brown, pink, black and orange.
Source :
www.monanneeaucollege.com/minerauxindex.htm
www.ganesha.be/min1.htm
http://myspace.eng.br/quim/quim1_009.asp#hist |
|
|
|
|